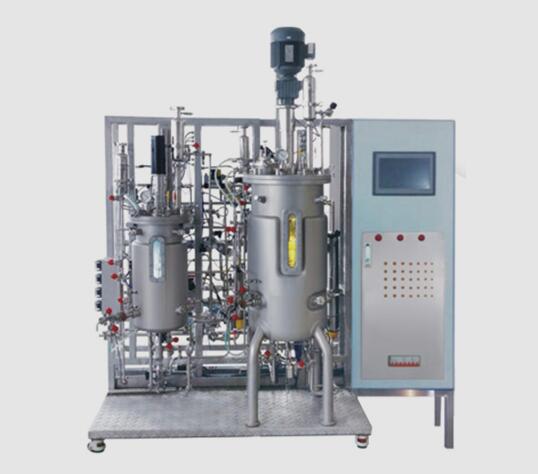
Introduction
Microbial fermentation is often different due to strains and products, but the general process is basically the same, usually including the preparation of bacteria, raw materials processing, vaccination, fermentation control and product extraction and other aspects.
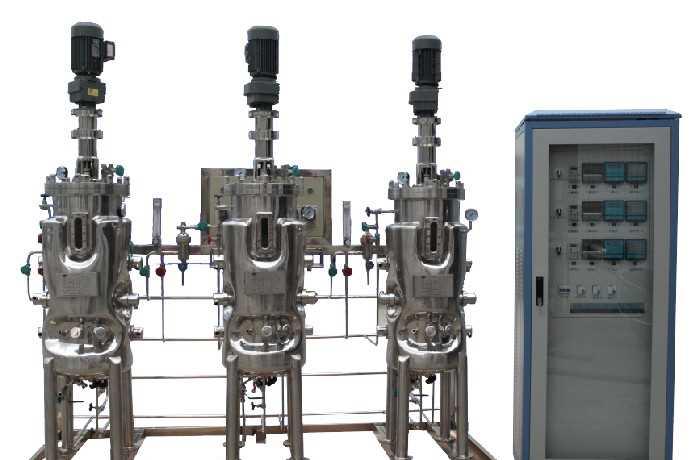

1. Strain preparation
Bacteria are the mother of fermentation industry, no bacteria, no microbial fermentation. Strains are generally divided into preservation strains, shake flasks (eggplant bottles, etc.), strains and seed tank strains. Preservation strains are the spare strains for fermentation, which are usually kept in low temperature drying. Preservation bacteria enter the production before inoculation, the first access ramp to activate, so that bacteria from dormancy to normal metabolic state. The medium used for activation is generally nutritious and easy to absorb, which is beneficial to the growth and propagation of bacteria. After the activation of bacteria and then expand the access flask (eggplant bottles) were cultured at the base of the preservation of culture medium is more extensive, more economical. Shake flask seed to further expand access to seed tank culture. The seed tank culture is closer to the culture medium used in the fermentor to allow the bacteria to adapt further to the culture medium of the fermentation medium. The seed can cultivate good after timely tank (ventilation Qushi) vaccination.2. Material handling
Fermentation materials are rich in raw materials, rich in ingredients and different in state. They can not be used directly by microorganisms. Therefore, pretreatment is necessary to be used as a component of culture medium for microbial fermentation. The fermented material is usually screened, crushed, cooked or hydrolyzed, and other related substances are formulated as fermentation medium.
3. Inoculation culture
After the fermentation medium is prepared, sterilization is carried out. After its cooling, timely vaccination. Vaccination should be carried out under sterile conditions to prevent contamination. Sterile inoculation is the key to the success of fermentation.
4, fermentation control
When the strains are connected, they provide the necessary growth conditions, and the bacteria begin to grow, reproduce, metabolize, ferment and accumulate metabolic products. Necessary production conditions include training temperatures, oxygen requirements, pH indicators, nutritional supplements, and foam removal. All these conditions should be observed, recorded, analyzed and improved regularly to ensure the normal production of fermentation. In the process of fermentation, the morphological changes of bacteria are often observed, and the accumulation of metabolites is measured to determine the optimum time for releasing the tank.
5, product extraction
Once the fermentation process is completed, product extraction is carried out in a timely manner. According to different products, different methods are adopted for separation and purification in order to obtain the highest yield and the best quality. Generally, the extraction methods include physical methods (such as filtration, centrifugation, drying, etc.), chemical methods (adsorption, distillation, chromatography, ion exchange, etc.) and biological methods, etc.
More Products